Can chronic inflammation be related to fat metabolism?
We are somehow used to the fact that mild chronic inflammation is a common part of our lives. Joints, tendons, adipose tissue and other tissues, usually poorly supplied with blood, sometimes cause us pain and problems. Sometimes over time, mild chronic inflammation stops hurting, but the pain may return or move, which is not right. I'm no expert on inflammation, so don't expect advice like what to lubricate, what to do, what herbs to use and similar advice. No, as always, I will try to find the causes, the complete basis, why inflammation, which is one of the main mechanisms for repairing damaged tissue, turns into something as incomprehensible and long-term devastating as chronic inflammation.
To understand, we will first easily outline the function of the immune system. This study, which deals with the connections between metabolism, redox state of the immune system and the course of inflammation, will help us to do this. As you may know, a cell obtains energy by making ATP molecules from available fuel. It may or may not use oxygen for this. It depends on the ambient conditions in which the cell is located. If there is not enough oxygen in a given place, it produces ATP from glucose (sugar) or glutamine, amino acids that are released during the breakdown of proteins. This occurs in cell plasma. The efficiency is much lower than in the production of ATP in mitochondria by so-called oxidative phosphorylation, but it allows the cell to gain enough energy very quickly. It's a process you know from preparing sauerkraut, it's fermentation. The glucose is processed into lactic acid.
Last time I showed you the importance of signaling with hydrogen peroxide from superoxide using the enzyme SOD (superoxide dismutase). Insufficient SOD activity slows down the burning of saturated fats and increases the level of mitochondrial superoxide. In addition, this condition is similar to the oxygen deficiency condition, in which the HIF (Hypoxia-Inducible Factor) is not degraded or oxygen deficiency is signaled with all possible consequences. We also revealed the cause of this condition, ie an excess of polyunsaturated fatty acids. These do not produce enough superoxide or the resulting hydrogen peroxide during their burning. This results in low SOD enzyme activity. Polyunsaturated fats, as they do not increase superoxide production, are burned preferentially as if they were ahead of the queue. Therefore, supplementing them may appear to be beneficial to health. They lower the level of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. But this is a big mistake of today's nutritional recommendations, because this myth only worsens the burning of all other fats, especially saturated fats. The body produces these itself and stores them as a supply of energy, which thus becomes unusable for the body.
(Correction, polyunsaturated fats produce a lot of superoxide, but this is taken out of the regulatory loop, causing ineffective control of fuel intake into the cell due to a metabolic bypass through the cytoplasm. The cell is thus overloaded with fuel, this causes a lack of NAD+ and rescue mechanisms are triggered through HIF-1α and pseudohypoxia.)
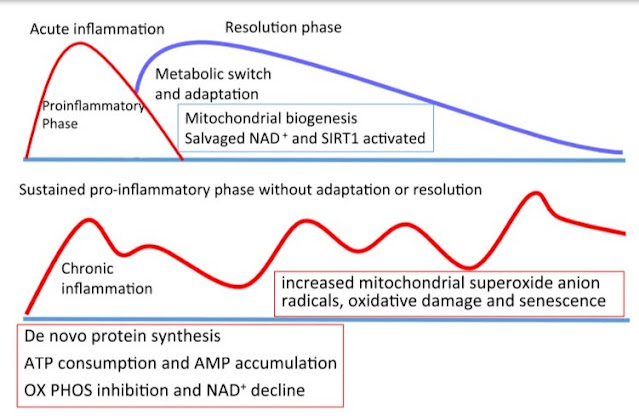
And it is this energy from saturated and monounsaturated fats that is the main source of energy to complete the inflammatory process. Do you understand? It is the "healthy" polyunsaturated fats from vegetable oils that support the development of chronic inflammation. When the first line of the immune system is done and wants to pass the scepter to the next line, this second line will not switch to gaining energy from burning fat. Instead, it signals the state of oxygen deficiency via HIF even in a situation where there is enough oxygen. Thus, the inflammation returns and again and again solves the situation by attacking an imaginary intruder and gains energy through fermentation (glycolysis). The process never completes, we have chronic inflammation.
Therefore, if we already know how chronic inflammation occurs, we can outline measures to prevent it. And these will be exactly the same measures that I mentioned in the previous post. See also older posts, everything revolves around cell metabolism. If any cell in the body suffers from a lack of energy, it will ask for more fuel, more blood glucose released from glycogen and more free fatty acids released from fat stores. But fat burning is slowed down, we have already clarified that. Unused free fatty acids must therefore be reassembled into triglycerides and stored in adipose tissue, but will be in other places, quite often near the sites affected by chronic inflammation. That makes a lot of sense, doesn't it? An increase in the level of free fatty acids and glucose will cause an increase in the level of insulin, we have insulin resistance. You can see that the cause of many chronic diseases is the same - an excess of vegetable fats from seeds, in our country it is mainly an excessive consumption of sunflower and rapeseed oil and seeds. Don't be afraid of animal fats, especially butter is a great treasure.
Although I initially said that I would not give any advice on topical products in a painful place, I will make an exception. You can easily make one such known lubricant for external use by ozonating olive oil with just a small ozone generator. E.g. let ozone from the generator bubble through 1 dl of quality olive oil for about 60 minutes. Although I do not know the nature of chemical reactions, there is a presumption that this oil locally can have similar effects as inhaled dilute hydrogen peroxide on the whole body, ie it will allow cells to gain the missing energy through beta oxidation of fats.
I will also add a few pictures from a study that clarifies in detail the mechanism of the transition of immune cells from fermentation metabolism to oxidative phosphorylation.
References:







Comments
Post a Comment