Ozone and nitric oxide, how do they interact?
I already covered ozone in an older post. If you don't read it, look there first. Today I will try to supplement the previous considerations with the hypothesis of how ozone is formed in a clean outdoor environment. Fresh air in a clean outdoor environment unencumbered by emissions, far from traffic and industry, contains quite stable concentration, typically around 0.1 mg of ozone in one cubic meter. All day long, even at night when the sun doesn't shine. Human exposure to ozone over a 24-hour period is therefore much higher in a clean natural environment than in the vicinity of emission sources burning fossil fuels. There, the concentration of ozone drops sharply after sunset, sometimes below 0.02 mg/m3. The measured data clearly show this.
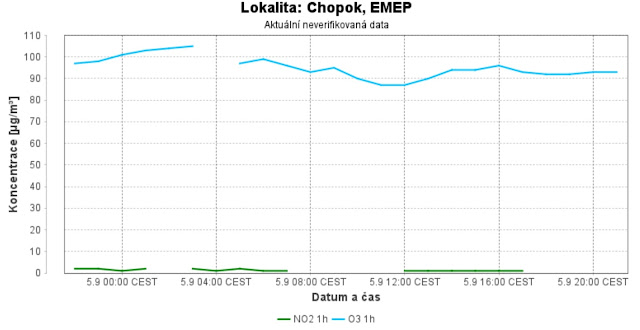 |
| Station on Mount Chopok in Slovakia on September 5, 2023, current measurement of O3 and NO2 in very clean nature |
 |
| Bardejov station in Slovakia on September 5, 2023, current measurement of O3 and NO2 in the urban environment. After sunset, ozone is used up for the oxidation of NO to NO2, the disappearance of NO2 by other chemical processes only takes place after a certain time. |
I don't understand the official emission rating system as exceeding daily O3 limits, not evaluating nightly decreases of ozone concentration values. Exceeding the daily limit is senselessly evaluated in this way, even in a completely clean environment, and it is supposely not strange to anyone. Let's see how ozone is formed in pure nature.
Soil bacteria are probably at the very beginning. Through their activity, they process (fix) atmospheric nitrogen. Just below the surface of the soil in symbiosis with the roots, they create nitric oxide (NO). Yes, the same one as in the previous post. Plants use it as a fertilizer, building material. The rate of NO formation depends on the time of day and year, especially on temperature and soil quality.
Part of the NO escapes from the soil, but it is not visible even when measuring the concentration of NO in the air. The presence of ground-level ozone immediately causes the oxidation of NO to NO2, which can already be measured well. When exposed to near-ultraviolet sunlight (λ < 400 nm), it decomposes into NO and atomic oxygen, which immediately binds to O2, thus forming ozone (O3). This O3 can then re-oxidize NO to NO2. Even a small amount of NO can thus generate enough O3.
NO + O3 -> NO2+ O2
NO2+ hv(λ<400 nm) -> NO + O
O + O2 + N2 -> O3 + N2
If a large amount of NO is not produced at night (e.g. by burning fossil fuels), ozone is kept at the same concentration and does not disappear. During the day, NO escapes from the soil and ozone is consumed to form NO2, but if the sun shines, it immediately takes care of restoring the ozone concentration. It seems to be arranged so that the ozone concentration is stable, not too high and not too low, ie 0.1 mg/m3. And I feel that we are adapted to this environment.
A lack of ozone in the interiors of modern buildings and in outdoor urban environments can probably lead to a reduction in our own NO production and reduced immunity. Ozone can react with NO in the nasal cavities and reduce its concentration. This, on the other hand, can increase the requirements for its production. This is my hypothesis, but since ozone therapy (performed by rectal insufflation) has been shown to increase blood NO levels in asthmatic patients and improve vasodilation, it would be worth investigating more. The official dogma that O3 in any concentration is toxic to the respiratory tract, I think it would be good to revise, I already wrote about it here.
A possible link to NO production is suggested. I don't know if ozone in the nasal cavities can, by oxidizing some of the nitric oxide to NO2, be a stimulatory signal to increase NO production. Purely on the basis of the rule that removing the product increases the production and thus increases the activity of the necessary enzymes, I would expect a positive effect of a concentration of 0.1 mg/m3 of ozone in the air on the production of NO in the nasal cavities and blood vessels. Ensuring a controlled concentration of O3 in modern interiors using some simple devices should not be a big problem. How would a study comparing the effect on health, especially on cell metabolism in older age, turn out? I haven't found any such study yet, which is a shame.
Supplement:
It appears that NO produced in the nasal cavities and atmospheric O3 are part of another regulatory loop that our civilization has "successfully" disabled. It is likely that O3 is used in the airways to detect oxygen sufficiency by NO oxidation. Oxygen itself is unsuitable for detection, there is too much of it in the air (21%). On the other hand, there is only very little of ozone (0.000005%), the more oxygen (ozone), the less NO we inhale and the more the blood vessels constrict, there is no need to send so much blood to the tissues, but if there is not enough oxygen (ozone), we inhale more NO and the vessels expand more, more blood is needed to the tissues. Additionally, there is a mechanism by which NO causes a slowing down of combustion, that is, a slowing down of oxidative phosphorylation (by blocking mitochondrial complex IV), presumably to conserve oxygen. But our body encounters a permanent lack of ozone in the modern environment, inhales too much of NO initially, and because it interprets this as a lack of oxygen, it finds that something is wrong and adapts over time. It reduces the production of NO by limiting the activity of the enzyme eNOS as we can see in the graph with age decreasing NO production and increasing vascular destruction. It is actually a rescue mechanism, although the slowed oxidation of the fuel has its consequences, e.g. insulin resistance.
It is the second regulatory loop for controlling the supply of oxygen to the tissues that has been eliminated by our civilization. That first regulatory loop is controlled by CO2 and is turned off by omega-6 vegetable oils, i.e. by overproduction of NADP+ by the enzyme 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase. It also first takes place as an over-activation, an excessively high rate of metabolism caused by the elimination of the glutathione-based antioxidant chain, with subsequent attenuation, enzyme acetylation and hypoxia as a rescue.
According to the Pareto principle, when we solve the most important problem, we solve 80% of all problems. If it continues to work, then if we also solve the second most important problem, we will solve up to 95% of all problems. I don't know, maybe if we restore these two regulatory loops that control the supply of oxygen to the tissues that have been discarded by civilization, it could solve up to 95% of the problems, i.e. the diseases of civilization.
References:
Seasonal dynamics and profiles of soil NO concentrations in a temperate forest
Aktuální hodinový přehled dat z automatizovaných stanic (neverifikovaná data)
Kinetic model of the inhibition of respiration by endogenous nitric oxide in intact cells




Comments
Post a Comment