Ozone (O3) has antioxidant effects. Are we missing it?
Ozone as an antioxidant? Oh no? It is a strong oxidizing agent! Toxic. The safe concentration in the air is set at just 120 micrograms per cubic meter. In the summer, we hear warnings that the level of ground-level ozone is too high, that is, in cities where there is a lot of pollution. So how is it?
I have already written several times on this blog that things are usually not so simple and straightforward, because the devil hides in the details. But it is interesting how dogma once established is persistently defended without taking into account more recent findings. So what about ozone?
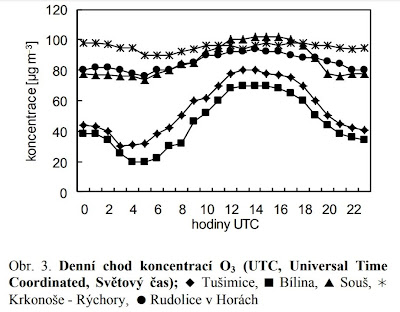
Take a look, for example, at this graph showing an example of the measured values of ground-level ozone in the Czech Republic, in the mountains and in cities.
Two typical daily curves can be seen on it, the lower one you might guess is from an environment with clean air, i.e. from a rural or mountain environment. But it's not, it's from industrial areas. From the mountains (about 3000 ft above sea level) and countryside are the upper curves, 80 to 100 micrograms per cubic meter. How is it possible? The citation from the paper about the cause:
"The reason is the fact that NO has a relatively short residence time in the air and in relatively clean rural areas, far from NO emission sources, there is no decomposition of O3 by nitric oxide. In these areas, O3 is removed from the air (in periods without precipitation) mainly only by the slow physical process of dry deposition."
So maybe we should rethink what the optimal ozone content is for a healthy environment, don't you think? In the mountains, the ozone content is relatively stable in summer (approx. 0.1 mg/m3) and does not decrease significantly even at night. It is lower only in winter, in the period of respiratory diseases. Why don't we know anything about it? But our ancestors apparently knew this or at least suspected it, placing sanatoriums for the treatment of respiratory diseases in the high mountain environment. They thought it was sunshine, but it was actually treating by ozone created by high-altitude ultraviolet radiation. Before the discovery of antibiotics, it was the only solution, used especially against tuberculosis.
Today we have studies that confirm that, at low levels, ozone stimulates immunity in the respiratory tract. But we still consider any amount of ozone in the air to be toxic. We think it will destroy our lungs, but that requires a much higher concentration. We can easily recognize it because we can smell ozone and if it irritates us to cough, it means that the concentration is too high. But I don't remember ever feeling the urge to cough in the mountains, not even after a storm, not even when it smells nice like fresh air. This does not mean that ozone is not dangerous. It is, but not in the concentrations found in pure nature. Ozone and smog, that's something else.
But what about the antioxidant powers? This must be some kind of nonsense, right? It isn't. Look at this.
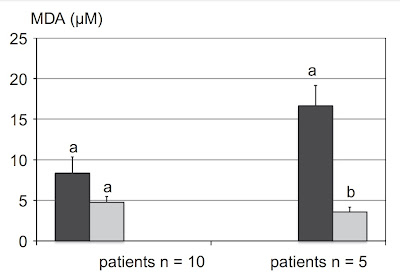
We have five groups of mice, control, diabetic (STZ), diabetic after ozone therapy, diabetic after oxygen therapy, and normal healthy mice after ozone therapy. It can be clearly seen that ozone therapy reduces the amount of hydrogen peroxide, but also MDA, poisonous fatty acid aldehyde that were formed by fat peroxidation. It also increases the level of reduced glutathione, the main antioxidant of the cell, increases the level of SOD, which is important for slowing down cancer growth, increases the level of catalase, but also decreases the level of glutathione peroxidase, which can correct the impaired regulation of fat breakdown and burning during fasting and between meals.
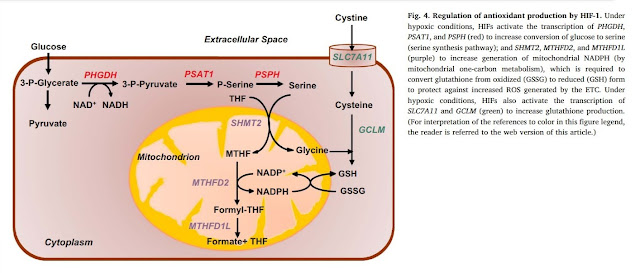
This study is from 2001, so it's been a while. There are also newer studies that show the mechanism by which the stimulation of the antioxidant environment in the cell is induced. We may be interested, for example, in the fact that the transcription factor HIF-1 also figures in this mechanism, the activation of which triggers, among other things, antioxidant protection. And HIF-1 is activated by increased production of superoxide O2- and hydrogen peroxide if there are problems in the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 in the electron transport chain. The same activation of antioxidant protection is also triggered by ozone, apparently already in a small concentration.
Of course, ozone is an oxidizing agent, but it stimulates protective processes in the cell so that the resulting effect is similar or even stronger than the use of antioxidants. It can thus stimulate the production of reduced glutathione GSH.
Ozone therapy is interesting, among other things, because it increases the expression of HIF-1α in tissues that need it, but decreases the expression of HIF-1α in tissues that have enough oxygen. Thus, using the example of damage to the rabbit cornea using the steroid MP (methylprednisolone), ozone therapy significantly reduces tissue damage by activating HIF-1α.
 |
| Effect of MP steroid and improvement after HIF-1α activation by ozone (MP+O3). |
Conversely, it reduces HIF-1α expression and kidney damage in a diabetic mouse model. Especially in combination of ozone therapy with insulin.
Model examples also show significant improvement in wound healing with ozone therapy. Or if ozone therapy is applied before an artificially induced heart attack in a rabbit model, the likelihood of damage to the heart muscle is significantly reduced.
As you can see, the given examples of the results of studies of ozone therapy effectiveness are very positive. What dosage is used and what are the supplementation methods? Due to the generally recognized toxicity of ozone for the lungs, e.g. rectal insufflation, such as a gas enema, is used. Or ozone is dissolved in the collected blood with an anticoagulant and the resulting mixture is administered intravenously. Doses of about 1 mg/kg of body weight are used in the studies mentioned. In ozone autohemotherapy, a dose of 270 ml of blood with a concentration of 0.02 to 0.08 mg/ml is used in humans, i.e. one dose is 5 to 20 mg of O3.
Let's calculate the approximate dose of ozone when staying in the fresh mountain air with a content of 0.1 mg/m3. A healthy adult exhales about 7 liters of air per minute. Sick easy double. This corresponds to approx. 1 mg of ozone, approx. 70% of which is absorbed, i.e. a total of 0.7 to 1.4 mg/day. The dose corresponding to ozone therapy is approx. 80 mg for a person weighing 80 kg. But this would mean that this dose corresponds approximately to the dose of ozone obtained over three summer months in healthy rural or mountain air. What do you think? Interesting, isn't it?
And I almost forgot about one more option, I already mentioned it here, it is ozonated olive oil for external use. If we blow ozone into 1 dl of oil from a 600 mg/h generator for an hour, we have 600 mg of ozone in the oil. This is enough for almost ten ozone therapies. Why not use it, it's simple. Or/and there is the possibility to inhale about 20 ml of a highly diluted hydrogen peroxide solution (0.1% to 0.3% H2O2) using a nebulizer, i.e. a dose of 20 to 60 mg of H2O2, probably with similar effects as O3. Ozone likely works by creating hydrogen peroxide and fatty acid peroxides in the blood, which serve as signals to trigger the production of antioxidants.
In addition, I believe that ozone can also act by another mechanism, namely by breaking down unsaturated fats at the place of unsaturated bonds and thereby creating saturated medium chains, e.g. two medium chains with nine carbons C9:0 (AzA) will form from oleic acid, because the formed ozonide in the presence of water breaks up into two shorter chains. It is thus probably possible to use ozone to break down all kinds of toxic metabolites with unsaturated bonds. This would explain the anti-cancer effects of ozone as well as the longer life expectancy in people living at higher altitudes where pure ozone is more likely to occur.
 |
| Ozone therapy lowers blood glucose levels in diabetic rats, alone and in combination with insulin. |
References:
Iva Hůnová - Přízemní ozón - Chemické listy 20180917
Ambient Ozone Primes Pulmonary Innate Immunity in Mice
Maintenance of redox homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factors
The effects of ozone therapy on caspase pathways, TNF-α, and HIF-1α in diabetic nephropathy
Ozone Uptake in Healthy Adult Males during Quiet Breathing
ADVANTAGES OF EXTRA VIRGIN OLIVE OZONIDE OIL COMPARED TO OTHER LIPID MATRICES










Comments
Post a Comment